Inherited Kidney Diseases: Types, Symptoms, and Management
By admin
Kidney health is vital to overall well-being, and when it comes to inherited kidney diseases, early detection and management can make all the difference. Inherited kidney diseases are a group of genetic disorders that can impact kidney function, leading to various health complications. Dr. Shashidhar Shree Niwas, a renowned nephrologist with over 25 years of experience, specializes in kidney disease management, dialysis, and transplantation. His expertise ensures that patients receive the highest standard of care.
What Are Inherited Kidney Diseases?
Inherited kidney diseases, also called genetic or hereditary kidney diseases, result from genetic mutations passed down through families. These conditions affect kidney structure and function, often leading to impaired filtration, fluid imbalances, and in severe cases, end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
While congenital kidney diseases are present at birth due to developmental abnormalities, inherited kidney diseases specifically stem from genetic mutations and may manifest at any age, depending on the condition.
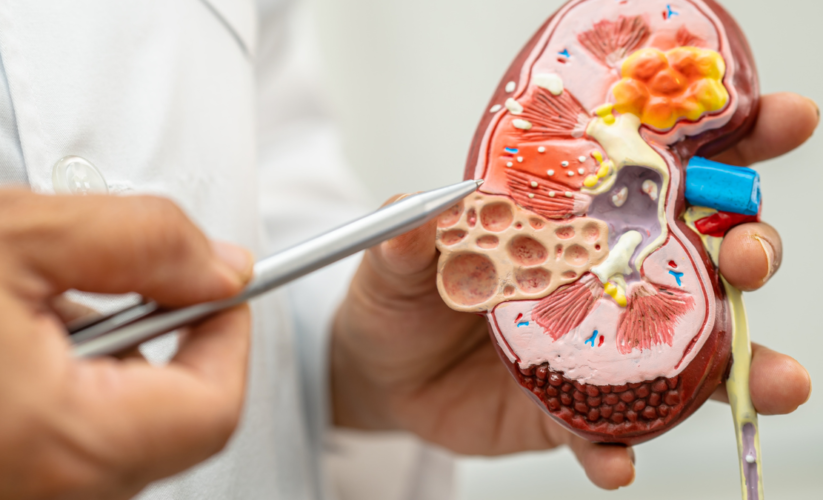
Types of Inherited Kidney Diseases
-
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD)
- Autosomal Dominant PKD (ADPKD): Commonly diagnosed in adulthood, this condition causes numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys, leading to organ enlargement and decreased kidney function.
- Autosomal Recessive PKD (ARPKD): Typically diagnosed in childhood, this form involves cysts in the kidneys and associated complications.
-
Alport Syndrome
This disorder affects the glomerular basement membrane, causing chronic kidney disease. Patients may also experience hearing loss and eye abnormalities. -
Fabry Disease
A rare genetic condition, Fabry Disease results in the accumulation of fatty substances in kidney cells, harming the kidneys and other organs. -
Autosomal Dominant Tubulointerstitial Kidney Disease (ADTKD)
A group of rare disorders primarily affecting kidney tubules and interstitial tissues, leading to progressive kidney dysfunction. -
Nephronophthisis
Chronic inflammation and fibrosis characterize this condition, often leading to kidney failure in children and adolescents. -
Medullary Cystic Kidney Disease (MCKD)
This rare disorder involves cyst formation in the kidney’s medulla, impairing function over time. -
Bartter Syndrome
This group of genetic disorders affects sodium and potassium reabsorption, resulting in electrolyte imbalances, muscle weakness, and potential kidney damage.
Symptoms of Inherited Kidney Diseases
The symptoms of inherited kidney diseases vary by type and severity but often include:
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): A common sign requiring careful management to prevent kidney damage.
- Proteinuria: Excess protein in urine, indicating kidney damage.
- Hematuria: Blood in urine, which may appear pink, red, or brown.
- Edema: Swelling in legs, ankles, feet, or face due to fluid retention.
- Fatigue: Caused by anemia linked to kidney dysfunction.
- Frequent Urination: Especially at night (nocturia).
- Pain or Discomfort: Abdominal or back pain, particularly in PKD.
- Kidney Stones: In some cases, inherited conditions lead to stone formation.
If these symptoms persist, consulting an experienced nephrologist like Dr. Shashidhar Shree Niwas is crucial for timely intervention.
Diagnosing Inherited Kidney Diseases
Detection of inherited kidney diseases involves a comprehensive medical and genetic evaluation, including:
- Family Medical History: Identifying patterns of kidney disease across generations.
- Physical Examination: Checking for signs like high blood pressure and swelling.
- Blood and Urine Tests: Assessing kidney function and detecting abnormalities like proteinuria or hematuria.
- Imaging Studies: Ultrasounds, CT scans, or MRIs to visualize kidney abnormalities.
- Genetic Testing: Advanced methods like Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) identify specific genetic mutations.
- Genetic Counselling: Understanding inheritance patterns and family planning implications.
Is Kidney Disease Always Hereditary?
Not all kidney diseases are hereditary. Many cases result from acquired conditions like diabetes, hypertension, infections, or medication side effects. However, recognizing hereditary kidney diseases is essential for targeted treatment and family risk assessment.
Managing Inherited Kidney Diseases
Although inherited kidney diseases cannot be cured, effective management can slow progression and improve quality of life. Key strategies include:
- Early Detection: Regular screening for individuals with a family history of kidney disease.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- A kidney-friendly diet low in sodium and protein.
- Adequate hydration and avoidance of nephrotoxic substances.
- Medical Management:
- Medications to control blood pressure and treat symptoms.
- Regular monitoring of kidney function.
- Dialysis: For advanced cases, dialysis helps maintain kidney function.
- Kidney Transplantation: Recommended in cases of ESRD, offering improved long-term outcomes.
- Emotional Support: Counseling and support groups to cope with the psychological impact of chronic kidney disease.
Trust Kidney Clinic for Expert Care
At Kidney Clinic by Dr. Shashidhar Shree Niwas, patients benefit from 25+ years of expertise in nephrology and kidney care. With a patient-centric approach, the clinic provides advanced diagnostic and treatment options, ensuring optimal care for inherited kidney diseases and other kidney-related conditions.
If you or a loved one is at risk of inherited kidney disease, seek expert consultation today. Early intervention is key to managing these conditions and safeguarding kidney health.
Contact Dr. Shashidhar Shree Niwas for a healthier tomorrow!